From the Humboldt County Department of Health and Human Services:
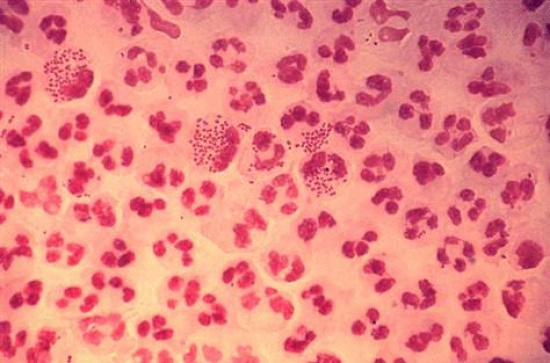
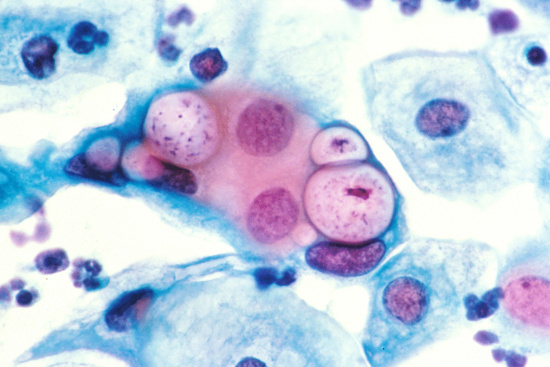
Gonorrhea is on the rise in Humboldt County and the Department of Health & Human Services (DHHS) is reminding people about the importance of getting tested.
Gonorrhea, which can be successfully treated if caught early, is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) in the U.S., with more than 800,000 infections estimated to occur each year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
“In Humboldt County, we have seen an increase in cases of both chlamydia and gonorrhea over the last three years, especially in the last three months,” said DHHS Public Health Nurse Eric Gordon.
From Jan. 1 through April 15 there have been 82 cases of gonorrhea reported to Public Health, according to DHHS’s Epidemiologist Ron Largusa. This trend represents a doubling of cases and rate from 2014 and a 10-fold increase in cases and rate from 2010.
Since 2010, the rate of gonorrhea has increased throughout California, recently reaching its highest point in a 20-year period. Regionally, a number of Northern California counties have experienced an increase in the number of gonorrhea cases over the last several years, Gordon said.
The infection is sexually transmitted and can also be spread from an infected pregnant mother to her child during delivery. To reduce the risk of contracting any STD, Gordon recommends that people get tested regularly, know their partner’s STD results before starting a new sexual relationship, always use condoms, and minimize anonymous sexual relations and sex with multiple partners.
While as many as 50 percent of gonorrhea cases show no symptoms, those that do most often present themselves in the following ways:
For men:
- A burning sensation when urinating
- A white, yellow, or green discharge from the penis
- Painful or swollen testicles (although this is less common).
For women:
- Painful or burning sensation when urinating
- Increased vaginal discharge.
- Vaginal bleeding between periods.
Gonorrhea can cause serious and permanent health problems if left untreated, the CDC states. In women, it can cause pelvic inflammatory disease which can cause complications, including:
- Formation of scar tissue that blocks fallopian tubes
- Ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the womb)
- Infertility
- Long-term pelvic/abdominal pain.
In men, gonorrhea can cause a painful condition in the tubes attached to the testicles. In rare cases, this may cause a man to be sterile. Although uncommon, untreated gonorrhea can also spread to blood or joints which can be life-threatening, according to the CDC.
One of the most important things that can be done to stop the spread of STDs is to ensure that all sexual partners who may have been exposed to the infection are notified. If someone is not comfortable notifying their partner(s), they can contact Public Health at 707-268-2174 to arrange for anonymous partner notification.
For more information and to get tested or treated, call your health care provider. You can also call the Public Health Clinic at 707-268-2108 to schedule an afternoon appointment. Free condoms are available at Public Health’s main office, 529 I St., as well as the Community Wellness Center, 908 Seventh St., both in Eureka. Free condoms are also available at Department of Health and Human Services offices in Garberville (727 Cedar St.) and Willow Creek (77 Walnut Way).
CLICK TO MANAGE